Istanbul Metro Network: A Complete Guide to Lines, Stations & Connectivity

The Istanbul Metro is one of the most advanced and expansive urban transport systems in Turkey, connecting the city’s European and Asian sides through a fast, reliable, and modern network.
Since the opening of its first line (M1) in 1989, the metro system has rapidly expanded to cover almost every major district, with over 150 stations in operation and many extensions under construction.
This article provides an in-depth look at the Istanbul Metro lines, station names, coverage areas, connection hubs, and practical tips for travelers and residents alike.

1. Overview of the Istanbul Metro System
The Istanbul Metro is operated by Metro İstanbul A.Ş., a subsidiary of the Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality.
The network spans both the European and Asian sides, forming the backbone of the city’s public transportation system.
Key Facts
- Total Length: Over 200 kilometers (as of 2024)
- Number of Lines: 11 lines in operation (M1A–M11), with several more under construction (M10, M12, M13, M14…)
- Number of Stations: Around 150+ active stations
- Operating Hours: Typically from 06:00 AM to 12:00 midnight
- Payment Method: Istanbulkart – a reloadable smart card usable across metro, tram, ferry, and bus services

2. Main Metro Lines in Istanbul
2.1 M1A & M1B – The Pioneer Line
The M1 Line was the first metro in Istanbul, opened in 1989, and later divided into two branches:
- M1A: Yenikapı – Atatürk Airport
- M1B: Yenikapı – Kirazlı
Notable Stations
- Yenikapı: Major interchange linking with M2, Marmaray, and ferry lines
- Aksaray: Connects to the T1 Tram line leading to Sultanahmet and the Grand Bazaar
- Bayrampaşa – Maltepe: One of the system’s original 1989 stations
2.2 M2 – The City’s Commercial Spine
Perhaps the most important metro line for visitors, the M2 Line runs from Yenikapı to Hacıosman, cutting through the city’s central business and entertainment areas.
Key Stations
- Taksim: Access to Taksim Square, Istiklal Street, and major hotels
- Şişhane: Gateway to Galata Tower and Karaköy district
- Levent & 4. Levent: Financial district with shopping malls (Kanyon, Özdilek)
- Gayrettepe: Deep underground station (72 m) and connection to M11 Airport Line
2.3 M4 – Kadıköy to Sabiha Gökçen Airport
Serving the Asian side, the M4 line stretches from Kadıköy on the coast to Sabiha Gökçen Airport, offering one of the most convenient airport links.
Highlights
- Kadıköy: A lively district full of cafés, restaurants, and ferry terminals
- Bostancı: Transfer point to sea ferries and suburban trains
- Sabiha Gökçen Airport: Direct metro access to Istanbul’s second international airport
2.4 M5 – The Driverless Line
The M5 Üsküdar–Çekmeköy Line is Turkey’s first fully automated driverless metro, connecting the Asian side’s residential zones to the Bosphorus shore.
Major Stops
- Üsküdar: Bosphorus waterfront, ferries, and Marmaray interchange
- Altunizade: Access to Emaar Square Mall
- Çekmeköy: Expanding residential and commercial area
2.5 M7 – The Modern Connector
Opened in recent years, the M7 Mecidiyeköy–Mahmutbey Line links busy residential and commercial areas in the European side.
It is also fully automated and known for its modern design.
2.6 M11 – Gayrettepe to Istanbul Airport
This high-speed metro line connects Gayrettepe (on M2) to Istanbul Airport, one of the world’s largest.
It’s part of the ongoing infrastructure expansion toward the new Business and Financial Zone in Arnavutköy.
3. Geographic Coverage
The metro system covers both sides of the Bosphorus:
European Side
Lines: M1, M2, M3, M7, M9, M11
Covers key districts such as Fatih, Beyoğlu, Şişli, Kağıthane, Başakşehir, Küçükçekmece, and Arnavutköy.
Asian Side
Lines: M4, M5, M8
Covers areas like Kadıköy, Üsküdar, Ataşehir, Maltepe, Pendik, and Kartal.
While both sides are connected via the Marmaray rail tunnel, the metro network itself is gradually expanding to allow cross-Bosphorus connectivity in the future.
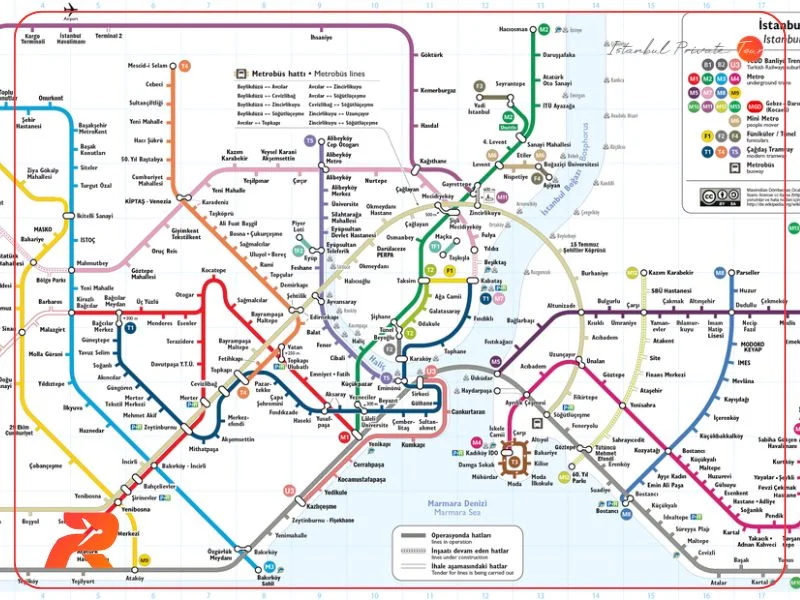
4. Major Interchange Stations
| Station Name | Connecting Lines | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Yenikapı | M1A, M1B, M2, Marmaray | Fatih |
| Gayrettepe | M2, M11 | Beşiktaş |
| Üsküdar | M5, Marmaray | Üsküdar |
| Kadıköy | M4, Tram, Ferry | Kadıköy |
| Mecidiyeköy | M2, M7 | Şişli |
| Kirazlı | M1B, M3 | Bağcılar |
These hubs make it easy to transfer between lines, trams, ferries, and bus networks across the city.
5. Advantages of Using the Metro
- Fast and punctual compared to surface traffic
- Affordable and cashless with Istanbulkart integration
- Safe and clean with modern facilities
- Direct connections to airports, shopping areas, and landmarks
- Ideal for tourists, covering almost all major attractions in Istanbul
6. Tips for Travelers
- Download the official metro map or use Google Maps for real-time navigation
- Avoid rush hours (08:00–10:00 & 17:00–19:00)
- Purchase and top up an Istanbulkart at vending machines inside every station
- Pay attention to direction signs — especially when transferring between M1A and M1B
- For airport routes: use M4 for Sabiha Gökçen and M11 for Istanbul Airport

7. Future Expansions
Istanbul continues to invest heavily in metro development.
By 2030, the network is expected to exceed 600 kilometers, becoming one of the largest in Europe.
Upcoming projects include M10 (Pendik–Sabiha Gökçen–Fevzi Çakmak), M12 (Ümraniye–Ataşehir–Göztepe), and M14 (Altunizade–Kazlıçeşme) lines.

Conclusion
The Istanbul Metro is more than a transportation system — it’s the lifeline of the city.
Efficient, affordable, and constantly evolving, it connects millions of residents and visitors daily across the vibrant metropolis that bridges two continents.
Whether you’re commuting to work or exploring Istanbul’s landmarks, the metro offers a fast, comfortable, and eco-friendly way to experience the city.
Similar Posts

Famous Cable Car Station In Istanbul
The cable car is a top tourist attraction in Turkey. In Istanbul, the cable car stations are bustling with people who want to see the city's most beautiful sights from a panoramic view. It's not just a fun way to get around; it's also a thrilling experience for solo travellers, families, and friends.

Istanbul Aquarium
Discover Istanbul Aquarium's thrilling activities: fish feeding, shark encounters, interactive experiences, diving pool, panoramic cinema, and more!


